Database sharding is a
technique of horizontal partitioning data across multiple physical servers to
provide application scale-out. SQL Database combined with database sharding
techniques provides for virtually unlimited scalability of data for an
application.
Sharding:
Sharding
is an application pattern for improving the scalability and throughput of
large-scale data solutions. To “shard” an application is the process of breaking
an application’s logical database into smaller chunks of data, and distributing
the chunks of data across multiple physical databases to achieve application
scalability. Each physical database in this architecture is what is referred to
as a shard.
- Scale out using tens, hundreds or thousands of database nodes using commodity hardware instead of expensive scale-up systems,
- To achieve scalable performance as the number of nodes increases,
- Build a solution with an excellent price-performance ratio derived from the use of commodity hardware instead of expensive application servers
- SQL Database provides a high availability SLA of 99.9% for all databases, no need to implement RAID and other availability techniques yourself.
How
to Shard your database
To start working with Sql server sharding I have used
SQLAzureMW tool to done sharding activity. You can download the tool from
Before starting sharding you need to design or update your
database keeping following points in mind
- Every table must have a primary key.
- Sharded key must be a primary key or part of primary key in related tables (Clustered index required).
- Identity and Timestamp are not included as a part of data types for sharded tables
- Identity can be set in Root DB tables and Sharding reference tables. (both terms defined during step by step creation)
- Root DB collation and size are replicated to all sharded databases.
- You need to manage schema changes in all databases manually to avoid merging problems.
- Replication not support with table scripts.
- Need to mention Federation key at table creation level even root database are not created yet (using this tool).
Run the tool and select Database
Connect to your local db where Database exists that needs to shard or migrate on SQL Azure
If you want to migrate to simple Azure DB select SQLAzure for Federation, Select as selected.
Also select objects like Tables, procedures etc.
You can also select Table and Schema or Table or Schema only.
Script generated for Selected objects and if there are any errors it will show in red lines in Summary section.
For federation as we don't connect our Azure server yet. We need to add federation key manually so that when script were executed at the end table are ready to created on the basis of federation key.
On this screen you can view FEDERATED ON (UserId = UserId).
- Federated On is keyword to add this table into federation
- "UserId" is key attribute on which we need to generated shards.
- "= UserId" is the Key column that has data and on the basis of this data definition shards data will be moved from one to other federation.
If you are planning to migrate your database onto Azure Plateform. You do not need to mention FEDERATED ON clause.
Use "Connect to Server" and by providing Azure credentials as we can see in next screen shot you will be connected to Azure Database server.
As there is no database created yet. We need a database or Root database to start our database migration.
Click on Create Database and You can et its size and Edition along with its name.
Following editions are available
- Express -- Web Editions
- Workgroup -- Business Editions
- Standard
- Enterprise
If you want to migrate your database without federation you can click next and deploy your changes to database.
for Federation:
You have successfully created Root database for your Federation database. Now connect again to create federations.
The difference is change your server type to SQL Azure Federation and mention your database that was recently created. In this case UserDBRoot
Now you have created Federation Root db and need to create it Federation Key on which you data will be moved to respective shards.
You can set Distribution data type as BigInt, Float and UniqueIdentifier.
Now you have successfully created Federation Member and you can see its range is Min value of BigInt to Max value of BigInt
In this Screen shot I am creating Split point that will be key decision factor to distribute data. For sample I have set to 5. (It depends on your requirements).
On click next scripts will generate member databases and also their respective table structures and data (if mentioned) using BCP command.
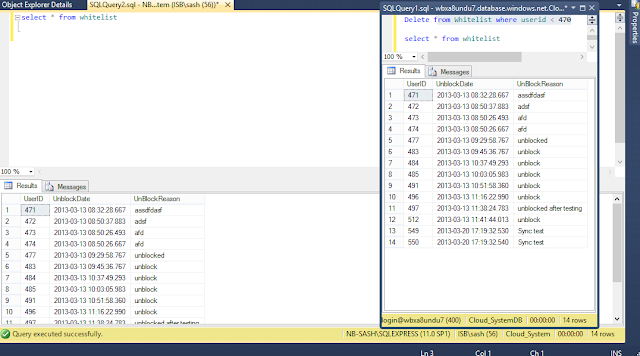
You can connect and query your database from Online Management Studio and Local management studio as well.
Merging Federated Members
If I want to merge my federation members I will use Delete button and specified options.
- For merging you need to remember
- All data of deleting member will be lost
- Take backup of both members (merger and deleting)
- After merging member you need to insert all deleted member data manually
- If you delete Federation all members will be lost
- You need to make your federation members offline to avoid problems to your customer
There will be another post that will define following in detail
- How to Query a specific Shard.
- How to Check database usage size.
- How to View your sharding database ranges and Stats by Query.
- Querying your database using Online and On-premises database management studio.